High-Yield Embryology Reference
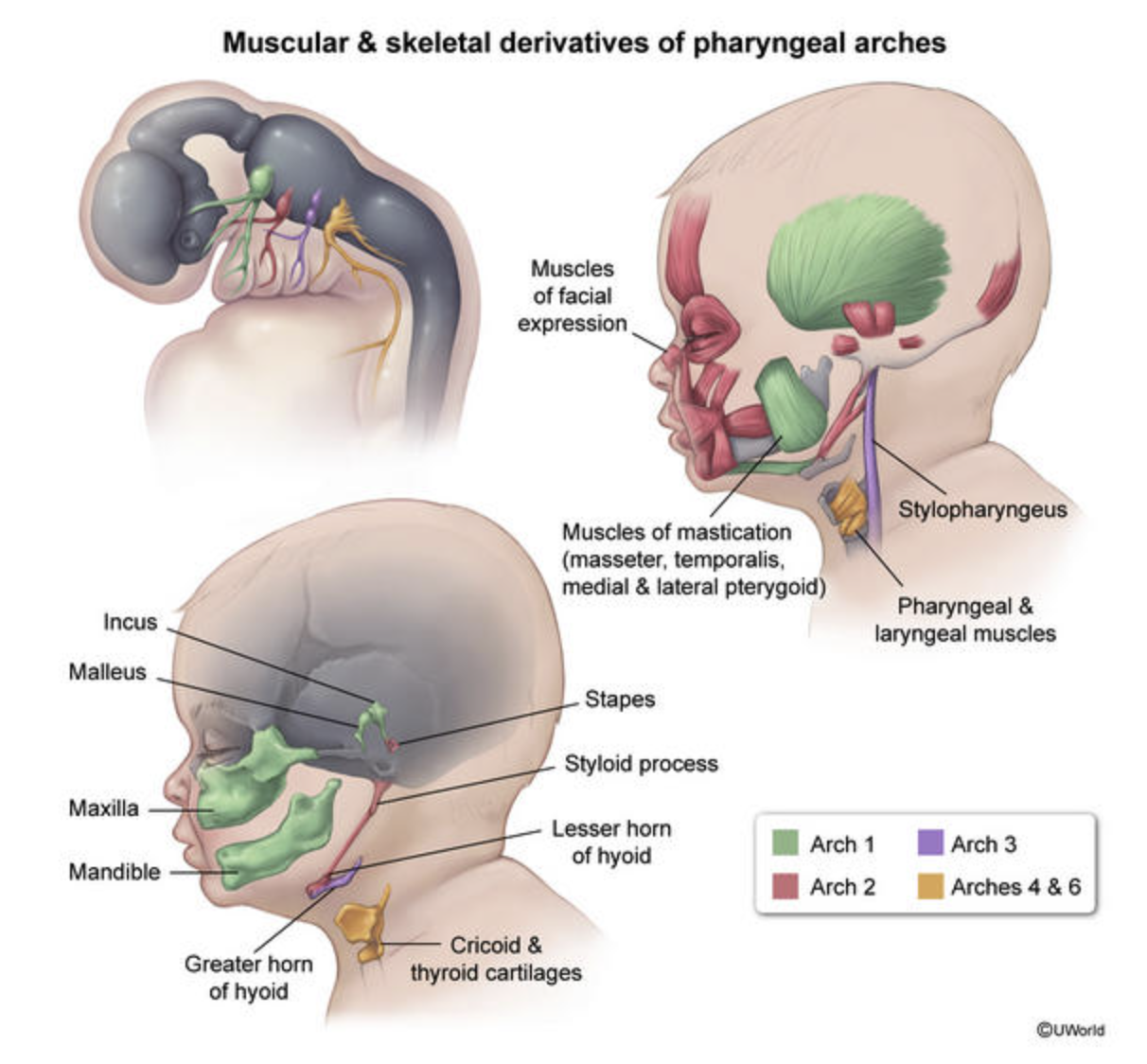
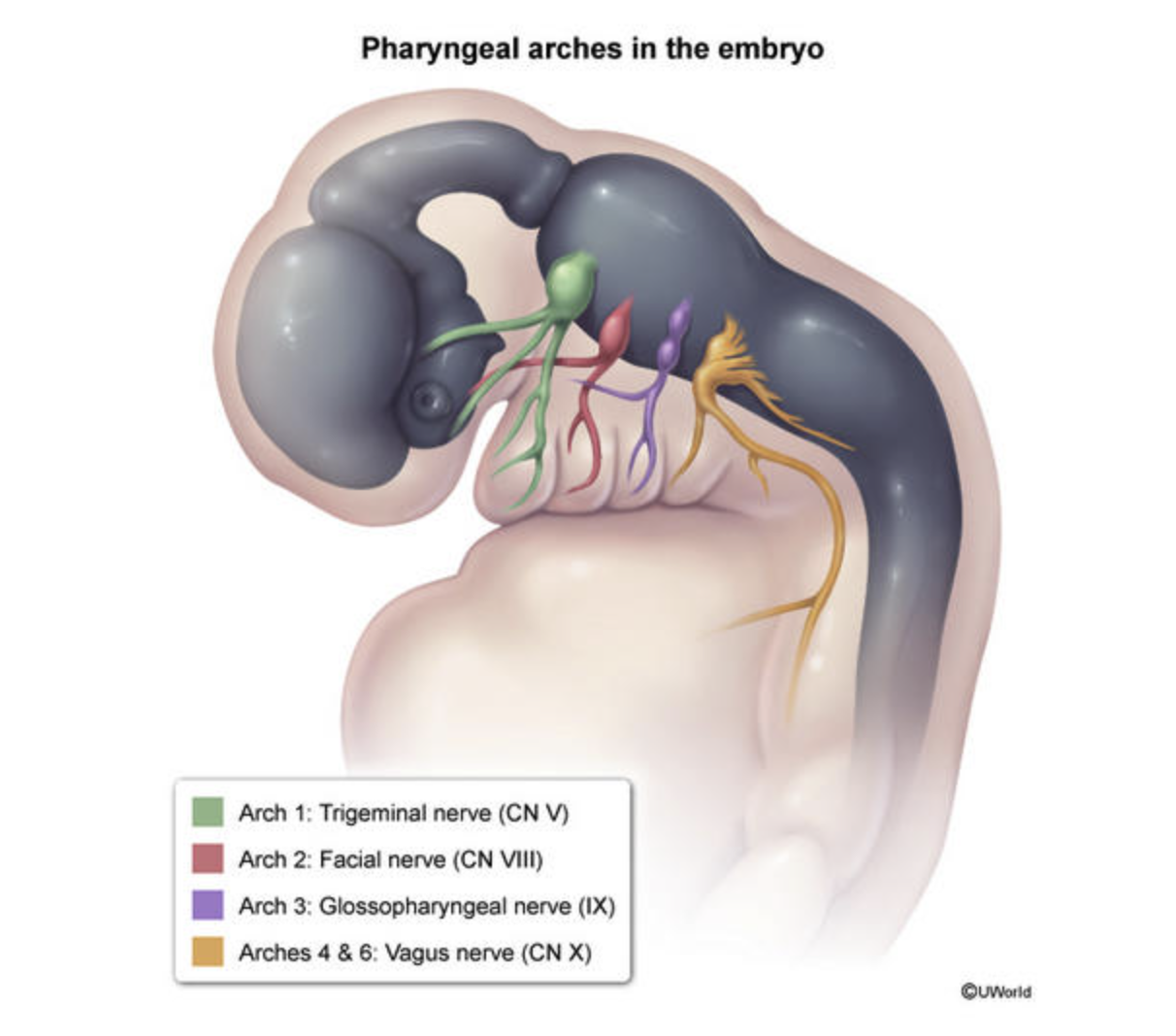
×1. Pharyngeal Arches (Mesoderm + Neural Crest)
Key Concept: Each arch has its own Cranial Nerve (CN), Muscle, and Cartilage/Bone.
Note: Arch 5 involutes and forms no major structures.
| Arch | Associated Nerve | Muscular Derivatives | Skeletal/Cartilage Derivatives | Clinical/Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | CN V3 (Trigeminal - Mandibular) | Muscles of Mastication (Temporalis, Masseter, Pterygoids), Mylohyoid, Anterior belly of digastric, Tensor tympani, Tensor veli palatini. | Meckel’s Cartilage: Mandible, Maxilla, Malleus, Incus, Zygomatic bone. | Mnemonic: M & T (Mandible, Mastication, Malleus, Meckel, Mylohyoid, Tensor). Defects: Treacher Collins Syndrome. |
| 2nd | CN VII (Facial) | Muscles of Facial Expression, Stapedius, Stylohyoid, Posterior belly of digastric, Platysma. | Reichert’s Cartilage: Stapes, Styloid process, Lesser horn of hyoid, Stylohyoid ligament. | Mnemonic: S (Stapes, Styloid, Smile, Stapedius, Seven). |
| 3rd | CN IX (Glossopharyngeal) | Stylopharyngeus (only muscle innervated by IX). | Greater horn of hyoid, Lower body of hyoid. | Provides sensory innervation to the posterior 1/3 of the tongue. |
| 4th | CN X (Vagus - Superior Laryngeal) | Pharyngeal constrictors, Cricothyroid, Levator veli palatini. | Thyroid cartilage, Epiglottic cartilage. | Used for swallowing (pharyngeal muscles). |
| 6th | CN X (Vagus - Recurrent Laryngeal) | All intrinsic muscles of larynx (except cricothyroid). | Cricoid cartilage, Arytenoid cartilage, Corniculate cartilage. | Used for speaking (laryngeal muscles). |
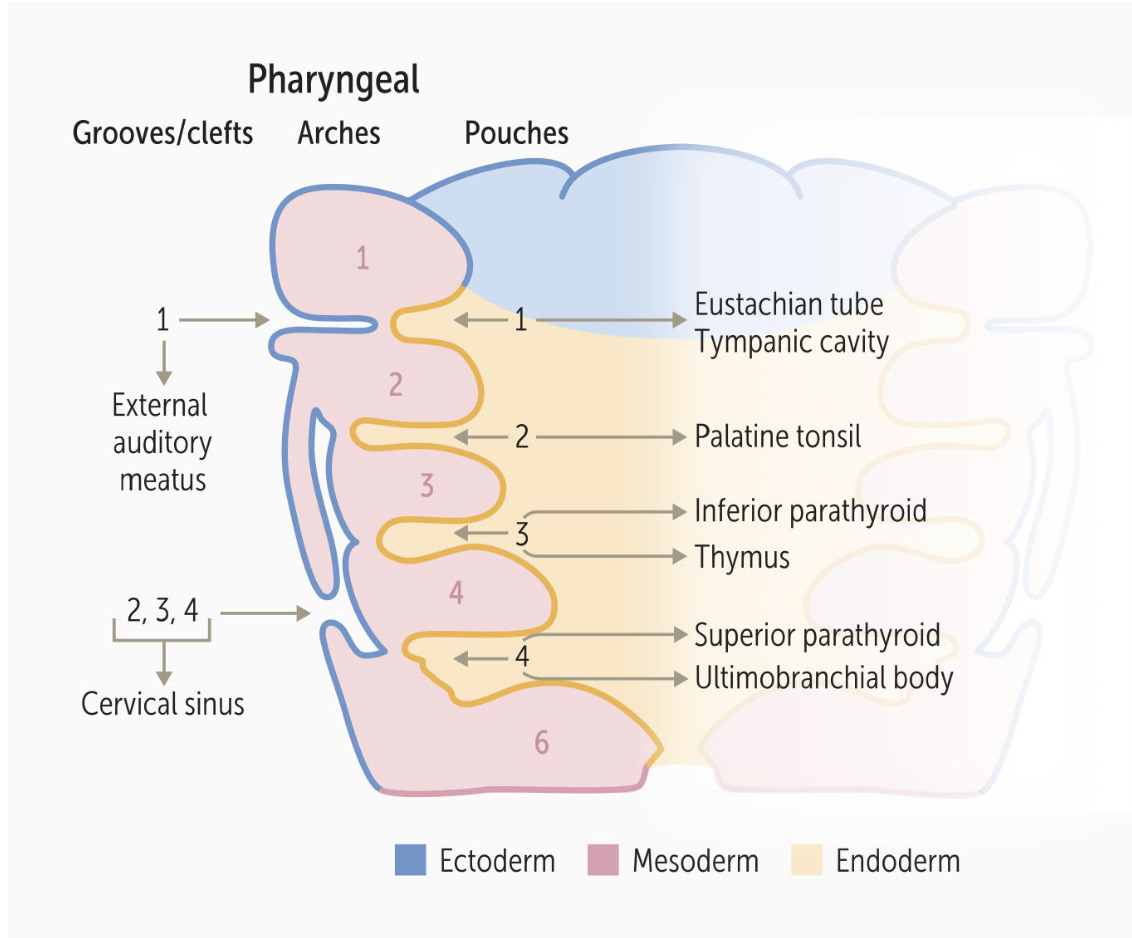
2. Pharyngeal Pouches (Endoderm)
Key Concept: These are lined by endoderm (inside the throat).
| Pouch | Derivatives | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | Middle ear cavity, Eustachian (Auditory) tube, Mastoid air cells. | Connects the pharynx to the ear. |
| 2nd | Epithelial lining of Palatine Tonsils. | Tonsillectomy bed is derived from this pouch. |
| 3rd | Inferior Parathyroids (Dorsal wing), Thymus (Ventral wing). | DiGeorge Syndrome (22q11 deletion): Failure of 3rd/4th pouch development → Thymic aplasia (T-cell deficiency) + Hypocalcemia (No parathyroids). |
| 4th | Superior Parathyroids, Ultimobranchial body (Parafollicular C-Cells of thyroid). | Note that Superior Parathyroids (from 4th) end up above Inferior Parathyroids (from 3rd) due to migration. |
3. Pharyngeal Clefts (Ectoderm)
Key Concept: These are lined by ectoderm (outside the neck).
| Cleft | Derivatives | Clinical Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | External Auditory Meatus (Ear canal). | The only cleft that persists as a normal adult structure. |
| 2nd - 4th | Normally obliterated. These clefts are covered by the expansion of the 2nd arch, forming the temporary Cervical Sinus, which then disappears. | Branchial Cleft Cyst: Persistent cervical sinus. Presents as a lateral neck mass (anterior to SCM muscle) that does not move with swallowing. |
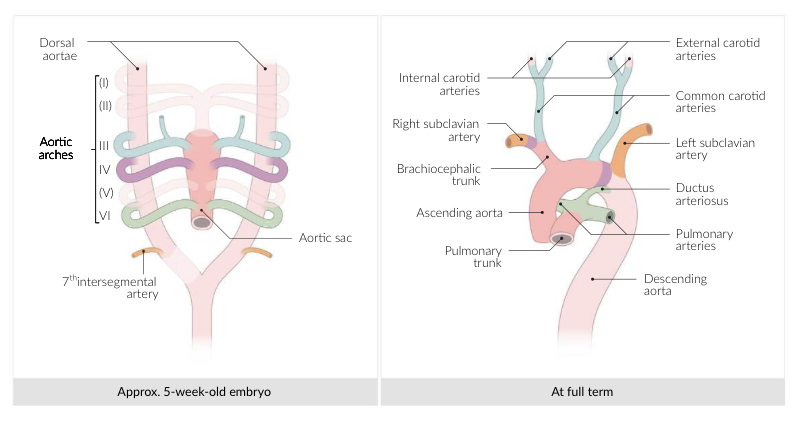
4. Aortic Arches (Arterial System)
Key Concept: These arteries run within the pharyngeal arches.
| Arch | Derivative | Mnemonic / Memory Aid |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | Maxillary Artery (branch of External Carotid). | Max is #1. |
| 2nd | Stapedial Artery (embryonic), Hyoid Artery. | Second = Stapedial. |
| 3rd | Common Carotid Artery, Proximal Internal Carotid Artery. | C is the 3rd letter of alphabet = Carotid. |
| 4th | Left: Arch of Aorta. Right: Proximal part of Right Subclavian Artery. |
4th Arch = 4 limbs (Systemic circulation). |
| 6th | Proximal: Pulmonary Arteries. Distal (Left only): Ductus Arteriosus. |
Pulmonary and Pulmonary-to-Systemic shunt. |
High-Yield Mnemonics & Tips
- CAP Layers:
- Clefts = Ectoderm
- Arches = Mesoderm (+ Neural Crest)
- Pouches = Endoderm
- Ear, Tonsil, Bottom-to-Top: (For Pouches 1-4)
- 1 (Ear) → 2 (Tonsil) → 3 (Inferior Parathyroid) → 4 (Superior Parathyroid).
- Thyroid vs. Branchial Cyst:
- Thyroglossal Duct Cyst: Midline, moves when you stick out tongue.
- Branchial Cleft Cyst: Lateral (anterior to SCM), does not move with tongue.
- Tongue Innervation (Matches Arches):
- Anterior 2/3 (Sensation): CN V3 (Arch 1).
- Anterior 2/3 (Taste): CN VII (Arch 2 - via Chorda Tympani).
- Posterior 1/3 (Sensation & Taste): CN IX (Arch 3).
- Root/Epiglottis: CN X (Arch 4).