×
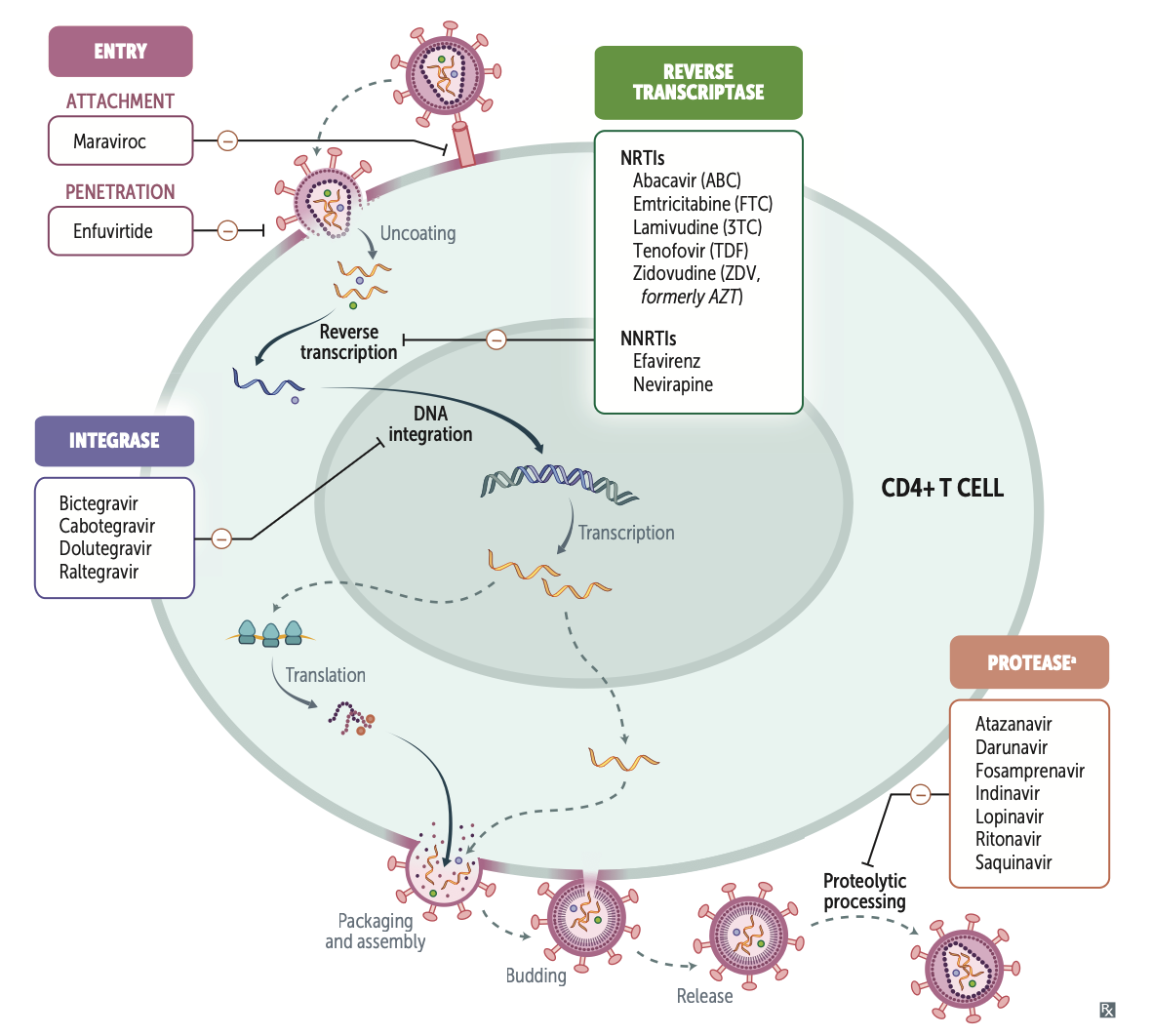
USMLE Step 1 HIV Reference
Diagram (Click to Zoom):

💡 USMLE Mnemonics:
- Abacavir = Abba (the band) sings "H.S.R." (Hypersensitivity Reaction).
- Efavirenz = Efing scary dreams (CNS symptoms).
- Nevirapine = Never have liver failure (Irony: It causes Hepatotoxicity).
- Zidovudine = Zzz (sleeping/tired) = Anemia/Bone Marrow Suppression.
Pharmacology Table
| Drug Class | Specific Drugs | Mechanism of Action | Adverse Effects / Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| NRTI (Nucleoside/tide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors) |
Abacavir (ABC) Didanosine (ddI) Emtricitabine (FTC) Lamivudine (3TC) Stavudine (d4T) Tenofovir (TDF) Zidovudine (ZDV/AZT) |
Competitively inhibit nucleotide binding to reverse transcriptase and terminate the DNA chain (lack a 3' OH group). Requires phosphorylation. |
Bone Marrow Suppression: Zidovudine. Pancreatitis: Didanosine, Stavudine. Peripheral Neuropathy: Didanosine, Stavudine. Lipoatrophy/Fat Redistribution: Stavudine. Renal Toxicity (Fanconi): Tenofovir (TDF). Hypersensitivity (HLA-B*5701): Abacavir. |
| NNRTI (Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors) |
Doravirine Efavirenz Nevirapine Rilpivirine |
Bind to reverse transcriptase at site different from NRTIs. Do not require phosphorylation. |
Rash (SJS/TEN): All NNRTIs (esp. Nevirapine). Hepatotoxicity: Nevirapine (Fulminant hepatitis). CNS symptoms/Vivid Dreams: Efavirenz. Teratogenic: Efavirenz (historic, now mostly considered safe but tested as unsafe). |
| Fusion Inhibitors | Enfuvirtide | Binds gp41, inhibiting viral entry. | Injection site reactions, pneumonia risk. |
| CCR5 Antagonists | Maraviroc | Binds CCR5 on surface of T-cells/monocytes, inhibiting interaction with gp120. | Upper respiratory tract infections, hepatotoxicity. *Requires tropism test.* |